Table of Contents
• Introduction: Elucidation of Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Etiology: Pervasive Triggers of Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Manifestations: Indications and Manifestations of Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Diagnostic Modalities: Techniques for Assessing Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Intervention: Non-Operative and Surgical Remedial Alternatives
• Homeopathic Remedies: Self-Care Measures for Mitigating Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Prophylaxis: Precautionary Measures for Preventing Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Physical Activity: Prescribed Exercises for Alleviating Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Pharmacotherapy: Medicinal Options for Managing Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Complementary Therapies: Alternative Treatment Modalities for Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Lifestyle Modifications: Adaptive Changes for Reducing Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Posture and Ergonomics: Significance of Posture and Ergonomics in Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Coping Mechanisms: Strategies for Coping with Sciatic Nerve Pain
• Conclusion: Synopsis of Managing Sciatic Nerve Pain
• FAQs: Frequently Posed Inquiries about Sciatic Nerve Pain
Introduction:
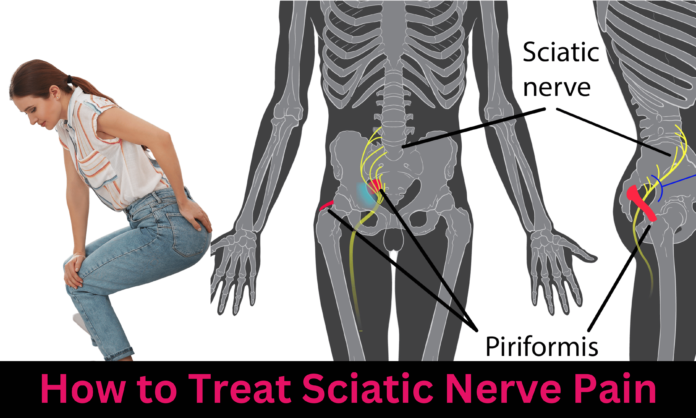
Sciatic nerve pain, also known as sciatica, is a prevailing condition that afflicts the sciatic nerve, which happens to be the longest and widest nerve within the human anatomy. It usually originates in the lumbar region and radiates down through the gluteal muscles and the lower extremity. The excruciating discomfort caused by sciatic nerve pain can be debilitating, posing significant challenges to one’s overall well-being and quality of life. In the subsequent discourse, we will delve into an array of treatment modalities that can be employed to effectively manage the distressing symptoms associated with sciatic nerve pain.
Causes:
The etiology of sciatic nerve pain can stem from a multitude of factors. The foremost culprit is often attributed to a herniated or bulging disc in the lumbar spine, leading to compression of the delicate sciatic nerve. Additional contributing factors may encompass spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, piriformis syndrome, trauma, and muscular imbalances. The intricate interplay of these underlying causes necessitates a comprehensive and tailored approach to managing the vexing symptoms of sciatic nerve pain.
Symptoms:
The manifestations of sciatic nerve pain can exhibit variability, contingent upon the site and severity of the ailment. Typical indications encompass a piercing, shooting discomfort that emanates from the lower back, traverses through the buttock, and travels down the leg. Additionally, numbness or tingling sensations, weakness in the affected leg, and challenges in leg mobility and control may be experienced.
Diagnosis:
Correct diagnosis is critical in developing an effective treatment strategy for sciatic nerve pain. The first step in identifying the ailment is usually a full assessment that involves a detailed medical history and a thorough physical examination. To determine the underlying source of the discomfort, diagnostic imaging procedures such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans may be indicated. Nerve conduction tests or electromyography (EMG) may be used to evaluate nerve function in certain circumstances.
Treatment:
The approach to treating sciatic nerve pain can vary based on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Non-surgical options may include physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and hot/cold therapy. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and corticosteroids may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. Alternative therapies such as yoga, massage, and herbal supplements may also be considered in certain cases.
In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options may include discectomy, laminectomy, and spinal fusion. These procedures aim to alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve and address the root cause of the pain.
Home Remedies:
Apart from medical interventions, there are several self-care strategies that can aid in the management of sciatic nerve pain from the comfort of home. These encompass maintaining proper posture, utilizing ergonomic furniture and equipment, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, applying heat or cold packs to the affected area, and engaging in gentle stretching exercises. By incorporating these practices into daily routines, individuals suffering from sciatic nerve pain can take proactive steps toward alleviating their discomfort.
Prevention:
Preventing sciatic nerve pain requires taking preventative steps. These are some preventative measures:
Keep appropriate posture: Sit and stand with proper posture to prevent tension on the lower back and avoid sciatic nerve compression.
Frequent physical activity, such as core strengthening and flexibility exercises, may help maintain the spine strong and flexible, lowering the chance of developing sciatic nerve discomfort.
Lift correctly: To prevent placing additional tension on the sciatic nerve, raise heavy things using your legs rather than your back.
Take pauses while sitting or standing for extended periods of time: If your employment requires you to sit or stand for long periods of time, take breaks and walk about to avoid putting too much pressure on your lower back and sciatic nerve.
Employ ergonomic furniture and equipment: Utilize ergonomic seats and workstations to support the natural curvature of the spine and encourage healthy posture. Chairs, keyboards, and monitors that are properly positioned may assist avoid pressure on the lower back and sciatic nerve.
Exercise:
Exercise on a regular basis may assist to manage sciatic nerve discomfort. But, it’s crucial to choose workouts that don’t make the discomfort worse. The following exercises are suggested for easing sciatic nerve pain:
Walking: Walking is a low-impact activity that doesn’t place too much stress on the back and may increase strength, flexibility, and circulation.
Swimming: Another low-impact activity that helps strengthen back muscles and ease sciatic nerve discomfort is swimming.
Yoga: For the management of sciatic nerve pain, gentle yoga positions that concentrate on strengthening and extending the back and core muscles might be helpful.
Pilates: Core-focused Pilates workouts may help reduce sciatic nerve discomfort by improving flexibility, stability, and posture.
Tai Chi: Tai Chi is a gentle, low-impact exercise that combines deep breathing with flowing motions. It is useful for reducing sciatic nerve pain since it may aid with balance, flexibility, and relaxation.
Medications:
Medication prescriptions are often used in the treatment of sciatic nerve pain in order to reduce the discomfort and inflammation brought on by this ailment. There are several possibilities for medicine, including:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen are examples of pharmaceuticals that effectively reduce pain and inflammation in the afflicted region.
Muscle relaxants: These drugs work to calm the muscles around the afflicted location, which may help to reduce discomfort and muscle spasms.
Corticosteroids: Injections or oral drugs containing corticosteroids may be recommended to treat sciatic nerve pain-related inflammation and discomfort.
Topical painkillers: To temporarily alleviate pain, menthol or capsaicin-containing creams, gels, or patches may be administered directly to the afflicted region.
Alternative Therapies:
In addition to traditional medical interventions, there are alternative therapies that may offer benefits in managing sciatic nerve pain. These therapies encompass:
Acupuncture: A technique that entails the insertion of slender needles into specific points on the body to assuage pain and stimulate healing.
Chiropractic care: Manipulative adjustments and spinal realignments administered by chiropractors can alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve by correcting misalignments in the spine.
Herbal supplements: Certain herbal supplements, such as turmeric, ginger, and devil’s claw, possess anti-inflammatory properties that could potentially reduce pain and inflammation associated with sciatic nerve pain. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider prior to taking any herbal supplements to avoid potential interactions with other medications. It’s always prudent to seek professional medical advice before incorporating any alternative therapies into your treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes:
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage sciatic nerve pain. Here are some tips:
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put added pressure on the lower back and exacerbate sciatic nerve pain. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the strain on the back and alleviate pain.
Quit smoking: Smoking can impair blood flow and decrease oxygen levels in the body, which can affect the healing process and increase inflammation. Quitting smoking can help improve overall health and reduce the risk of worsening sciatic nerve pain.
Practice stress management techniques: Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and exacerbate sciatic nerve pain. Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and alleviate pain.
Use proper footwear: Wearing shoes that provide proper support and cushioning can help alleviate pressure on the lower back and sciatic nerve. Avoid wearing high heels or shoes with minimal support for extended periods.
Sleep in a comfortable position: Sleeping in a position that supports the natural curvature of the spine, such as on your back with a pillow under your knees, can help reduce pressure on the lower back and alleviate sciatic nerve pain.
Conclusion:
Pain along the sciatic nerve is very debilitating and may have a serious influence on a person’s quality of life. But, sciatic nerve pain may be successfully treated and prevented with the right kind of therapy and certain tweaks to one’s way of life. Maintaining excellent posture, exercising regularly, using required drugs and alternative treatments, making appropriate modifications to one’s way of life, and learning stress management strategies are all essential for reducing discomfort and promoting healing. It is critical to work with a healthcare practitioner to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to the individual’s requirements. Always check in with your doctor before beginning a new treatment plan, including physical activity or medication.
FAQs:
Can sciatic nerve pain go away on its own?
Sciatic nerve pain can resolve on its own in some cases, especially with proper self-care and conservative treatments. However, it’s important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How long does sciatic nerve pain last?
The duration of sciatic nerve pain can vary depending on the severity and underlying cause. It can last from a few days to several weeks or even months in some cases.
How about working out if I have sciatic nerve pain?
Managing sciatic nerve pain may be aided by light workouts and stretches that don’t make things worse. Nonetheless, it’s crucial to talk to a doctor or fitness expert about which workouts are safe and effective for you.
Can stress contribute to sciatic nerve pain?
Yes, chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and exacerbate sciatic nerve pain. Practicing stress management techniques can help reduce stress and alleviate pain.
Can I stop sciatica from coming back?
Absolutely, using stress management strategies, changing your lifestyle, keeping up a decent posture, and getting regular exercise may all help avoid the recurrence of sciatic nerve discomfort. To create a thorough preventative strategy, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion:
preventive steps including keeping excellent posture, routine exercise, utilizing prescription drugs and alternative treatments when necessary, altering one’s lifestyle, and employing stress-reduction tactics may all help to successfully cure and prevent sciatic nerve pain. Always seek the advice of a healthcare professional to ensure correct diagnosis and care, as well as to create a personalized treatment plan that is tailored to your specific requirements. It is possible to reduce the pain and suffering brought on by sciatic nerve pain and enhance the overall quality of life with the right treatment and management. Hence, take action to manage your sciatic nerve discomfort and live pain-free!
Please take note that this information is not meant to replace consultation with a doctor. For the correct diagnosis and treatment of any medical issue, always visit a healthcare professional. I appreciate your reading.
Follow us on our social media channels.